In the relentless pursuit of efficiency and competitive advantage, businesses are turning to a new breed of digital assistants: AI agents. These are not your average chatbots. We’re talking about sophisticated, goal-oriented systems capable of autonomous decision-making and action. They are the unseen workforce, operating behind the scenes to streamline internal operations and, in turn, supercharge employee productivity. From automating tedious administrative tasks to providing insightful data analysis, AI agents are poised to revolutionize the way we work. This article delves into the transformative power of AI agents in internal operations, exploring their applications, the tangible benefits they deliver, and the crucial considerations for their successful and responsible implementation.
Section 1: The Rise of the AI Agent: More Than Just Automation
For years, automation has been a key driver of business process improvement. However, traditional automation tools are often rule-based and limited in their ability to handle complex, dynamic tasks. Enter the AI agent. Unlike their predecessors, AI agents are equipped with advanced capabilities like natural language processing, machine learning, and reasoning. This allows them to understand context, learn from experience, and make independent decisions to achieve a predefined goal.
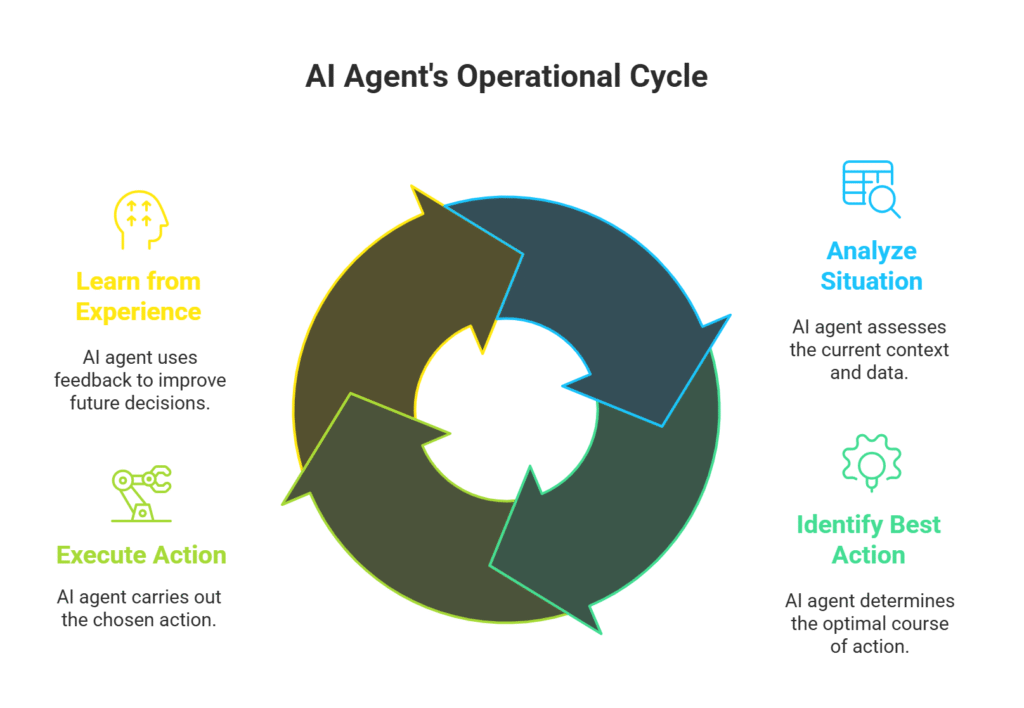
Think of an AI agent as a highly intelligent and proactive team member. It doesn’t just follow a script; it analyzes situations, identifies the best course of action, and executes it. This autonomy is what sets them apart and makes them so powerful. They can manage complex workflows, interact with multiple systems, and even collaborate with human colleagues to complete tasks.
The impact of this technology is already being felt across various internal departments:
- Human Resources (HR): AI agents are transforming HR by automating repetitive tasks such as screening resumes, scheduling interviews, and answering frequently asked questions from employees. This frees up HR professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives like talent development and employee engagement. For example, an AI agent can intelligently screen thousands of resumes, identifying the most qualified candidates based on predefined criteria, and then schedule interviews with hiring managers, all without human intervention.
- Finance: In the finance department, AI agents are streamlining processes like invoice processing, expense report management, and financial data analysis. They can automatically extract data from invoices, match them with purchase orders, and route them for approval, significantly reducing manual effort and the risk of errors. Furthermore, AI agents can analyze financial data to identify trends, detect anomalies, and provide valuable insights to support better decision-making.
- Information Technology (IT): IT helpdesks are often inundated with repetitive requests. AI agents can act as the first line of support, resolving common issues like password resets and software installation requests. This not only provides employees with instant support but also allows IT staff to focus on more complex technical challenges. AI agents can also proactively monitor IT infrastructure, predict potential issues, and even perform routine maintenance tasks, ensuring the smooth operation of business-critical systems.
- Project Management: AI agents are also making their mark in project management. They can assist with task allocation, progress tracking, and resource management. By analyzing project data, they can identify potential bottlenecks, suggest corrective actions, and provide real-time updates to project managers, ensuring projects stay on track and within budget.
Section 2: The Tangible Benefits: A More Productive and Engaged Workforce
The integration of AI agents into internal operations is not just about automation; it’s about augmenting the capabilities of the human workforce and creating a more productive and engaged work environment. By taking over mundane and time-consuming tasks, AI agents empower employees to focus on higher-value activities that require creativity, critical thinking, and strategic decision-making.

The benefits are multi-faceted:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: This is perhaps the most immediate and tangible benefit. By automating repetitive tasks, AI agents can significantly reduce the time and effort required to complete them, leading to a substantial increase in overall efficiency and productivity. Case studies have shown that organizations can achieve significant time and cost savings by deploying AI agents in their internal operations.
- Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors: To err is human, but in business, errors can be costly. AI agents can perform tasks with a high degree of accuracy, minimizing the risk of human error in data entry, calculations, and other routine processes. This not only improves the quality of work but also reduces the time and resources spent on rework and error correction.
- Enhanced Employee Experience: When employees are bogged down by tedious administrative tasks, it can lead to frustration and burnout. By offloading these tasks to AI agents, organizations can create a more positive and rewarding work experience. Employees can then focus on more engaging and meaningful work, which can lead to increased job satisfaction and higher retention rates.
- Faster Decision-Making: AI agents can analyze vast amounts of data and provide real-time insights, enabling faster and more informed decision-making. For example, a finance manager can use an AI agent to quickly analyze sales data and identify emerging trends, allowing them to make timely decisions about pricing and inventory management.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike human employees, AI agents can work around the clock, providing continuous support and ensuring that critical processes are always running smoothly. This is particularly beneficial for global organizations with teams spread across different time zones.
Section 3: The Path to Success: Responsible and Strategic Implementation
While the potential benefits of AI agents are undeniable, their successful implementation requires careful planning and a strategic approach. It’s not simply a matter of plugging in a new technology. Organizations must consider the technical, ethical, and human aspects of integrating AI agents into their workplace.
Here are some key considerations for a successful and responsible implementation:
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: It’s often best to start with a pilot project in a specific department or for a particular process. This allows the organization to test the technology, measure its impact, and learn from the experience before rolling it out more broadly.
- Choose the Right Use Cases: Not all tasks are suitable for automation by AI agents. It’s important to identify the processes that are most repetitive, time-consuming, and rule-based. These are the areas where AI agents can deliver the most value.
- Prioritize Data Quality and Security: AI agents are only as good as the data they are trained on. Organizations must ensure that they have high-quality, clean data to train their AI models. Data security and privacy are also paramount, and robust measures must be in place to protect sensitive information.
- Foster a Culture of Collaboration: It’s crucial to communicate openly and transparently with employees about the introduction of AI agents. Emphasize that these agents are tools to augment their capabilities, not replace them. Encourage a culture of collaboration between humans and AI, where each plays to their strengths.
- Invest in Employee Training and Reskilling: As AI agents take over more routine tasks, the skills required of human employees will evolve. Organizations must invest in training and reskilling programs to equip their workforce with the skills needed to work effectively alongside AI. This includes skills in areas like data analysis, critical thinking, and strategic problem-solving.
- Address Ethical Considerations: The use of AI raises important ethical questions about bias, fairness, and accountability. Organizations must establish clear ethical guidelines for the development and deployment of AI agents to ensure that they are used responsibly and do not perpetuate existing biases.
- Embrace a Human-in-the-Loop Approach: For many tasks, the optimal approach is a “human-in-the-loop” model, where AI agents handle the bulk of the work, but human oversight and intervention are available when needed. This ensures that critical decisions are still made by humans and that there is a mechanism for correcting errors.
The future of work will undoubtedly be a collaborative one, where humans and AI agents work together to achieve common goals. By embracing this new reality and taking a strategic and responsible approach to implementation, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI agents to boost employee productivity, drive innovation, and gain a significant competitive edge in the years to come. The era of the unseen workforce has arrived, and its impact is just beginning to be felt.



