The year 2025 has cemented itself as a definitive inflection point in the history of business-to-business (B2B) sales.
We have officially transitioned out of the era of “digitally enabled” sales, which was defined by static CRM databases and manual email sequencing.
We have now entered the era of Agentic Artificial Intelligence.
This shift is not merely an incremental improvement in efficiency; it is a fundamental restructuring of the economic physics that govern lead generation and prospecting.
Current market data indicates that AI adoption has moved from the experimental fringe to the operational core of high-performing revenue organizations.
Approximately 56% of sales professionals now utilize AI daily.
Crucially, these adopters are statistically twice as likely to exceed their quotas compared to their non-AI-using counterparts.
This correlation underscores a growing divergence in the market between those mastering these tools and those falling behind.
Organizations that successfully operationalize AI are achieving non-linear gains in productivity and revenue.
Conversely, laggards face rapidly rising customer acquisition costs (CAC) and diminishing returns on traditional outreach.
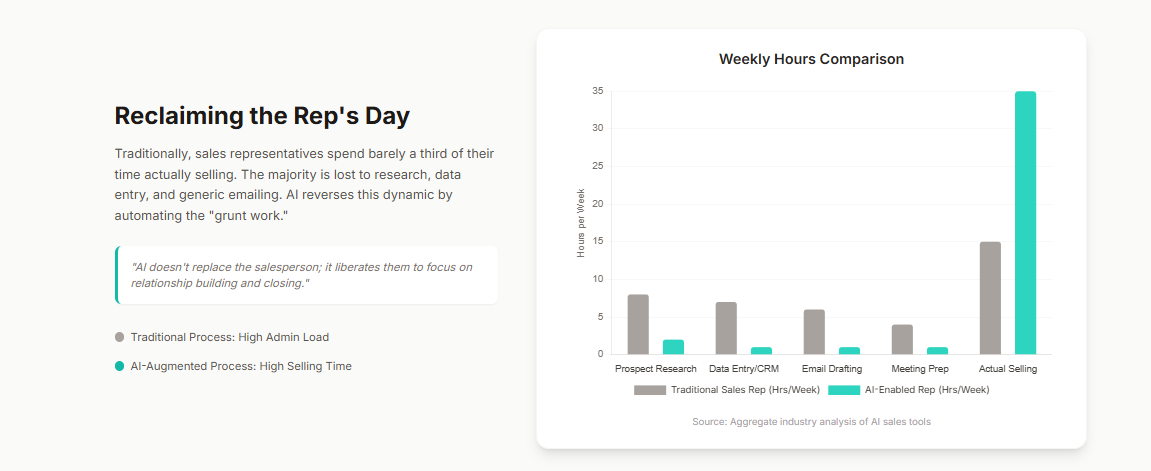
The capabilities of AI have matured from simple generative tasks—such as drafting email copy—to fully autonomous execution.
“Digital Workers” or “AI SDRs” (Sales Development Representatives) now operate 24/7.
They autonomously identify prospects, conduct deep research, orchestrate multi-channel outreach, and negotiate early-stage qualification hurdles.
These agents do not sleep, do not suffer from rejection fatigue, and can scale activity volume by factors of 10x to 20x compared to human equivalents.
However, this explosive growth brings a complex set of challenges, including the “Efficiency Paradox” and strict data governance requirements.
This guide provides an expert-level analysis of the state of AI in sales prospecting for 2025, offering a rigorous framework for implementation.
The Paradigm Shift: From Assistive Copilots to Agentic Autonomy
To understand the current state of the market, one must analyze the rapid evolutionary trajectory of Sales AI.
We have progressed through three distinct phases in less than five years.
These are the Assistive Phase (2020-2022), the Generative Phase (2023-2024), and the current Agentic Phase (2025 and beyond).

The Limitations of the Copilot Era
In the Assistive and Generative phases, AI functioned primarily as a “Copilot.”
Tools utilized Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist human users with discrete, isolated tasks.
A salesperson might prompt an AI to “write an intro email for a CFO” or summarize a call transcript.
While valuable, this paradigm kept the human strictly in the driver’s seat for every action.
The human remained the bottleneck.
The cognitive load of switching context, prompting the AI, and reviewing the output limited the scalability of these solutions.
The Architecture of Agency
The breakdown of the human bottleneck characterizes the Agentic Phase.
In 2025, AI systems are designed as autonomous agents capable of independent reasoning and execution loops.
Unlike a chatbot that waits for input, an agent is goal-directed.
It is given an objective—”Fill the pipeline with qualified leads from the manufacturing sector”—and it determines the steps to achieve that goal.
This autonomy is powered by a sophisticated architectural loop often described as Perception-Cognition-Action.
1. Perception (The Sensory Layer):
The agent continuously monitors external data streams. It “sees” when a target account hires a new VP or “reads” a news article about company expansion.
2. Cognition (The Reasoning Layer):
Utilizing advanced reasoning models, the agent synthesizes these perceptions. It forms a hypothesis, such as determining that a recent funding round indicates a need for specific software.
3. Action (The Execution Layer):
The agent executes the strategy without human hand-holding. It interfaces with APIs to send emails, connect on LinkedIn, and update CRM records.
The Rise of the AI SDR
The most visible manifestation of agentic AI is the “AI SDR.”
This is a category of software designed to function as a fully autonomous digital employee.
Startups like 11x, Artisan, and Landbase have pioneered this space.
These agents are marketed as “digital workers” with names like “Alice” or “Ava.”
They possess distinct personas and specialized roles, such as outbound prospecting or inbound lead response.
A single AI SDR can perform the workload of 5 to 10 human SDRs.
They operate 24/7 across all time zones with zero “ramp time.”
This introduces a new form of leverage in sales organizations: Asynchronous Productivity.
While the human sales team sleeps, the digital workforce continues to research, qualify, and book meetings.
Table 1: Human SDR vs. AI SDR Capabilities
Operational Metric |
Human SDR |
AI SDR (e.g., Alice, Ava) |
Strategic Implication |
Daily Capacity |
50 – 100 activities |
1,000+ activities |
Massive volume scaling. |
Availability |
40 hours/week |
168 hours/week (24/7) |
Instant speed-to-lead globally. |
Cost Structure |
$75k – $125k/year |
$7k – $45k/year |
>80% reduction in OpEx. |
Ramp Time |
3-4 Months |
Hours to Days |
Agility to pivot strategies instantly. |
Data Handling |
Prone to error |
Real-time logging |
Improved forecast accuracy. |
The Technological Landscape: Platforms and Players
The market for AI prospecting tools in 2025 is bifurcated between agile, specialized startups and massive, integrated enterprise platforms.
Revenue leaders face a strategic choice between “best-of-breed” point solutions and “all-in-one” ecosystems.
The Autonomous Specialists
Companies like 11x and Artisan represent the bleeding edge of the AI SDR market.
11x focuses on “Digital Workers” like Alice (outbound) and Julian (inbound).
Alice mimics human behavior patterns on LinkedIn to avoid spam filters.
Julian addresses the “speed-to-lead” problem by initiating voice calls within minutes of a form submission.
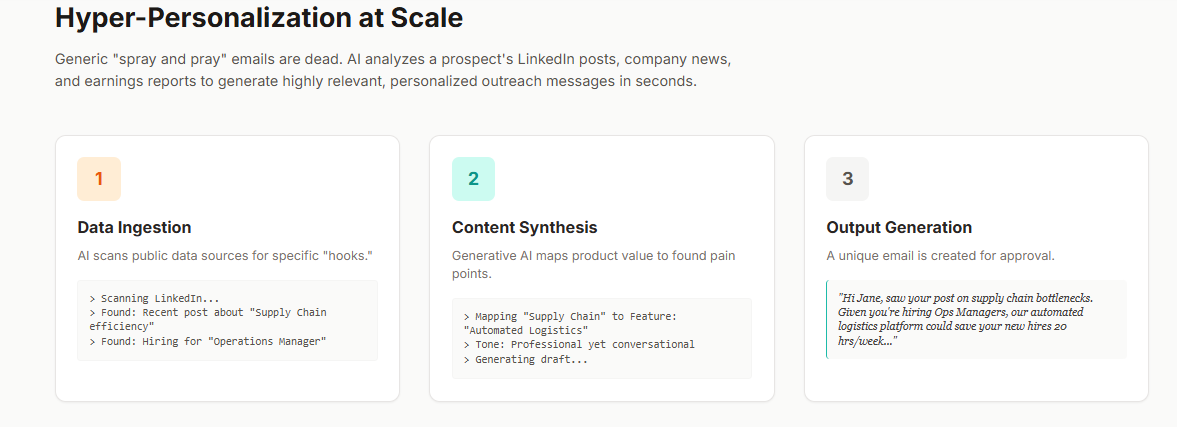
Artisan offers “Ava,” a BDR that consolidates the entire outbound stack.
Ava utilizes a “Personalization Waterfall” to analyze data points like news and tech stack changes.
This allows her to construct messages that feel bespoke, reducing the “robotic” feel of lesser tools.
The Enterprise Juggernauts
Salesforce leverages its massive data gravity to capture the enterprise segment with Agentforce.
The primary barrier to enterprise AI adoption is data security.
Agentforce solves this via the “Einstein Trust Layer.”
This masks sensitive data before sending it to an LLM and checks output for toxicity.
It allows enterprises to deploy autonomous agents without risking data leakage.
Furthermore, these agents live within the Customer 360 ecosystem.
An agent can pause outreach if it detects a high-severity support ticket in Service Cloud, offering superior context.
HubSpot competes with Breeze AI, focusing on the mid-market and ease of use.
Breeze embeds AI deeply into the workflow, allowing for the automation of content creation and lead scoring.
Organizations have used Breeze to increase content production by over 200%, driving organic traffic for prospecting agents to convert.
The Data Infrastructure: Fueling the Engine
In 2025, the adage “garbage in, garbage out” has become a lethal reality for sales teams.
An AI agent is a multiplier; if fed bad data, it will multiply errors and reputational damage at scale.
Consequently, the data enrichment market has become the most critical layer of the sales stack.
The “All-in-One” vs. “Modular” Philosophy
RevOps leaders must choose between consolidated databases and modular orchestration.
Apollo.io exemplifies the consolidated database model.
It offers a massive proprietary database of over 275 million contacts combined with execution tools.
It is fast and cost-effective, but data accuracy can be a bottleneck.
In high-volume AI campaigns, even a small bounce rate can degrade domain reputation.
Clay represents the modular, waterfall enrichment model.
Clay is not a database; it is a data orchestration platform.
It integrates with over 100 data providers.
When a user requests an email, Clay triggers a “waterfall”: checking Provider A, then Provider B, and so on.
This method yields data accuracy rates of 95%+, which is critical for protecting email deliverability.
Clay also features “Claygent,” an autonomous web scraper that performs deep research tasks no static database can match.
Predictive Intelligence and the “Dark Funnel”
Beyond contact data, AI is revolutionizing prioritization through predictive analytics.
Platforms like 6sense and Bombora track “intent signals.”
They monitor activity across the B2B web to identify companies researching relevant solutions.
In 2025, this data is fed directly into AI SDRs.
An agent can autonomously detect an intent signal and trigger an immediate, context-aware outreach sequence.
This ability to intercept the “Dark Funnel” significantly shortens sales cycles.
Operationalizing the Engine: Governance and Ethics
The transition to an AI-led sales motion is a change management challenge.
Successful organizations follow a rigorous implementation framework to mitigate risks.
The “Human-in-the-Loop” (HITL) Framework
Blindly trusting autonomous agents is a recipe for disaster.
The most effective deployments use a HITL model, especially in early stages.
-
Shadow Mode: For the first 2-4 weeks, the AI identifies leads and drafts emails but does not send them. Humans review drafts to calibrate tone.
-
Confidence Thresholds: Systems use scoring. If confidence is high (95%), it sends automatically. If low (70%), it routes to a human for approval.
Risks and Ethical Considerations
The autonomy of AI agents introduces significant risks that require robust governance.
Algorithmic Bias:
AI models trained on historical data can amplify past biases.
If an organization historically ignored certain regions, the AI might “learn” to deprioritize them systematically.
Regular “fairness audits” of lead scoring models are essential.
Privacy and Compliance:
GDPR and CCPA require strict consent management.
AI agents must honor “Do Not Sell” requests and Global Privacy Control signals.
An agent that ignores a suppression list can trigger massive fines.
Hallucinations:
If an agent invents a product feature to build rapport, reputational damage is instant.
Best-in-class systems use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to restrict the AI to verified knowledge bases.
The Efficiency Paradox
The efficiency of AI creates a paradox.
As the marginal cost of sending a personalized email approaches zero, volume has exploded.
Buyers are inundated with AI-generated emails, leading to “Inbox Saturation.”
Conversion rates for standard outreach are plummeting as buyers develop “AI blindness.”
Success in 2025 depends on Signal-Based Selling.
This means reaching out only when a specific, high-intent trigger occurs, rather than general list-based blasting.
Checklist for AI Sales Implementation:
-
[ ] Audit Data Hygiene: Clean CRM data before connecting any AI agent.
-
[ ] Select Architecture: Choose between All-in-One (Apollo) or Modular (Clay).
-
[ ] Define Guardrails: Set strict RAG parameters to prevent hallucinations.
-
[ ] Shadow Mode: Run the agent in draft-only mode for 14 days.
-
[ ] Train the Human: Evolve SDRs into “AI Orchestrators” who manage the system.
Conclusion
In 2025, AI in sales prospecting is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a present-day operational reality.
The organizations that win will not be those that simply buy the tools.
Victory belongs to those who master the data infrastructure and implement rigorous governance.
They must successfully evolve their human talent to work alongside their digital counterparts.
The era of “spray and pray” is dead.
The era of algorithmic precision has arrived.