Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept from the pages of a sci-fi script; it’s a powerful tool that is actively reshaping the landscape of film and television. Rather than replacing the screenwriter, AI has emerged as the most significant evolution in the writer’s toolkit since the word processor, acting as a collaborator, analyst, and production powerhouse.
This technology is poised to fundamentally alter the economics and creative workflows of Hollywood, with its most immediate impact being felt in the critical rewriting phase.
The financial momentum behind this shift is undeniable. The global market for AI in film is projected to explode from $1.4 billion in 2023 to over $14.1 billion by 2033. The AI screenwriting software segment is on an even more dramatic trajectory, forecasted to grow from about $2 billion in 2024 to an incredible $46 billion by 2031. This isn’t a distant trend; it’s happening now.
In 2023, reports indicated that over 45% of film studios were already integrating AI into their workflows. This rapid adoption, however, has sparked intense debate, culminating in the landmark 2023 Writers Guild of America (WGA) strike, which sought to define the relationship between the human creator and the machine.
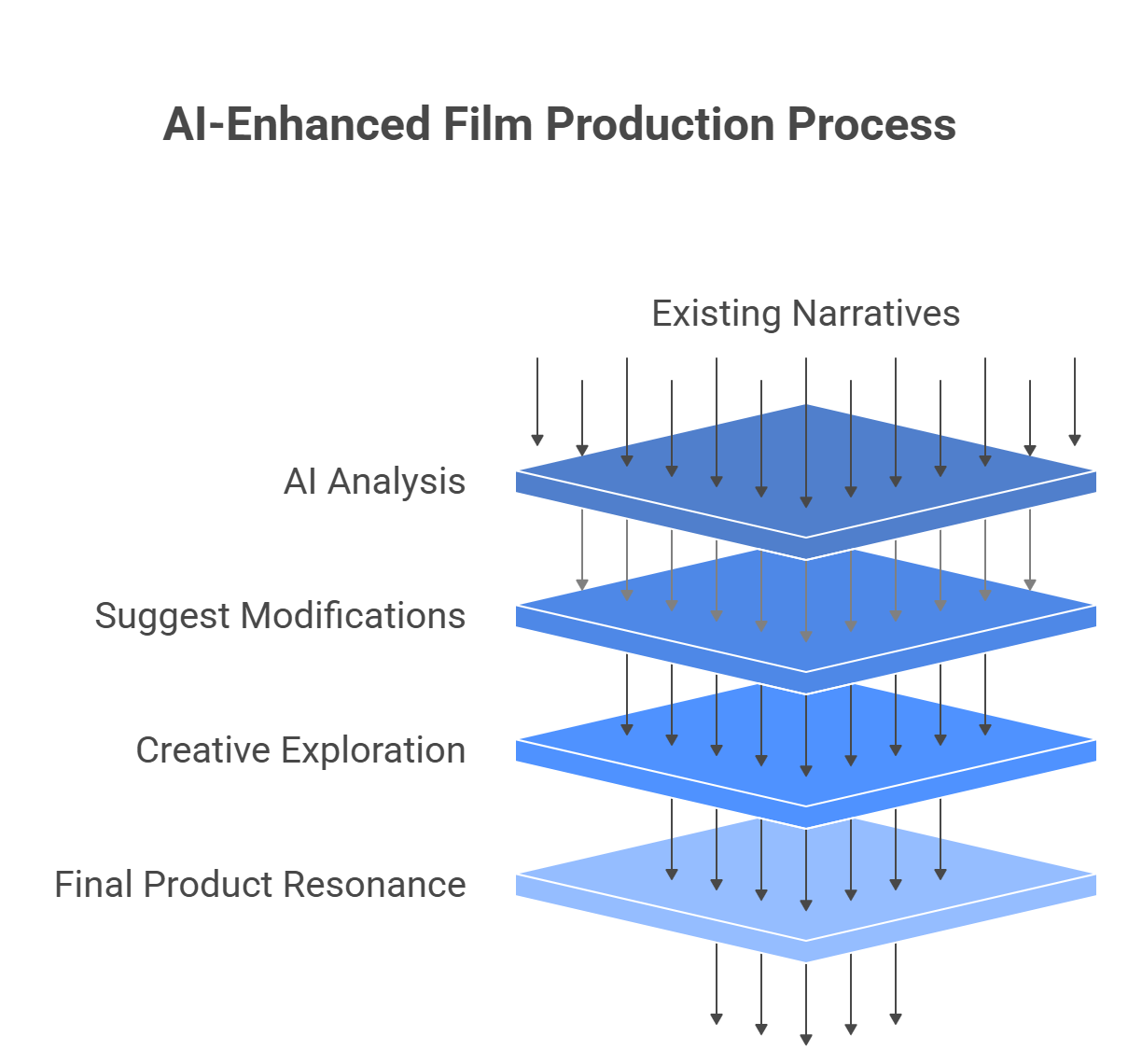
The true significance of this technological revolution lies in a deeper transformation. By integrating AI, the screenplay evolves from a static creative document into an intelligent, machine-readable asset. It becomes the dynamic blueprint that can streamline and automate huge portions of the pre-production pipeline, making the act of rewriting the first step in building a smarter, more efficient film.
Summary of the article in the form of an audio podcast
The AI Co-Pilot: Deconstructing the Rewrite Process
The rewrite is where a good story becomes a great one. It’s a meticulous process of refining structure, polishing dialogue, and sharpening character arcs. It is in this granular, iterative work that AI has become an invaluable creative partner, moving beyond simple grammar checks to become an active collaborator. These tools augment and accelerate the human writer’s vision, tackling specific challenges that turn a rough draft into a production-ready screenplay.
Enhancing Dialogue and Character Voice
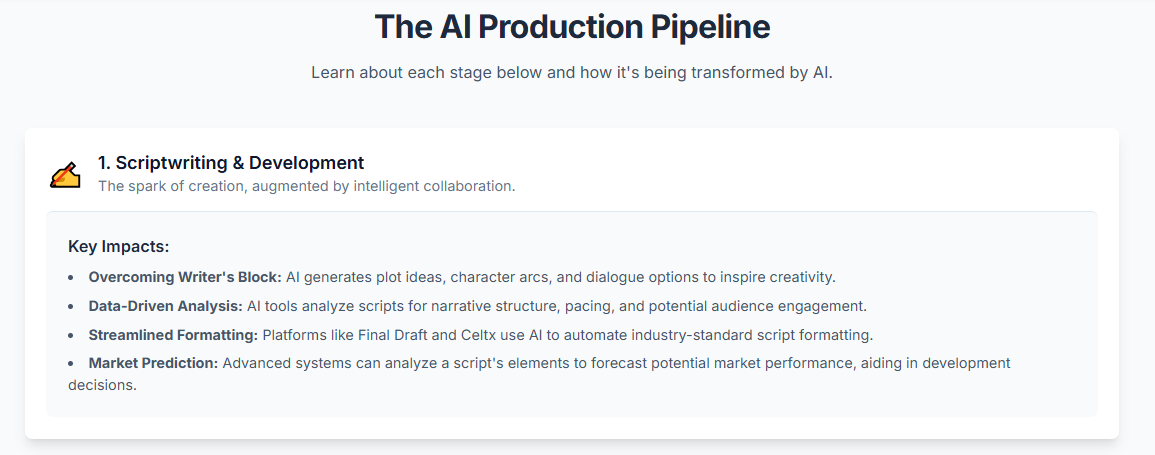
One of the most powerful applications of AI is in refining dialogue. Trained on vast libraries of successful scripts and literature, AI algorithms can analyze dialogue for authenticity, flagging lines that feel unnatural or inconsistent with a character’s established personality. Tools can offer alternative phrasing or generate new lines tailored to a specific tone—be it witty, dramatic, or suspenseful—ensuring each character maintains a distinct voice. This allows a writer to quickly test different approaches to a scene, refining the subtext and emotional impact with a speed that manual rewriting simply cannot match.
Mastering Structure and Pacing
Beyond the line-by-line level, AI excels at structural analysis. A writer can feed a draft into an AI platform and receive almost instant feedback on its narrative architecture. These systems can identify potential plot holes, track character arcs for consistency, and pinpoint pacing issues where the story might drag. For writers facing a creative block, the AI can act as a tireless brainstorming partner, suggesting alternative plot developments or new scene ideas to reignite momentum. This function isn’t about dictating the story, but about presenting possibilities that serve as a springboard for the writer’s own ingenuity.
The Human-in-the-Loop Model
Crucially, the effective use of these tools relies on a human-in-the-loop model. The writer remains the ultimate arbiter, providing the creative vision, emotional core, and cultural context that the machine lacks. The AI handles the data-intensive tasks—pattern recognition, option generation, and structural analysis—while the writer curates, refines, and integrates the suggestions. Best practices emphasize using the technology to challenge assumptions and explore new creative avenues, with the writer’s instinct as the final authority. This collaborative dynamic redefines the creative process, turning the writer into a prompter, curator, and editor of a sophisticated creative partner.
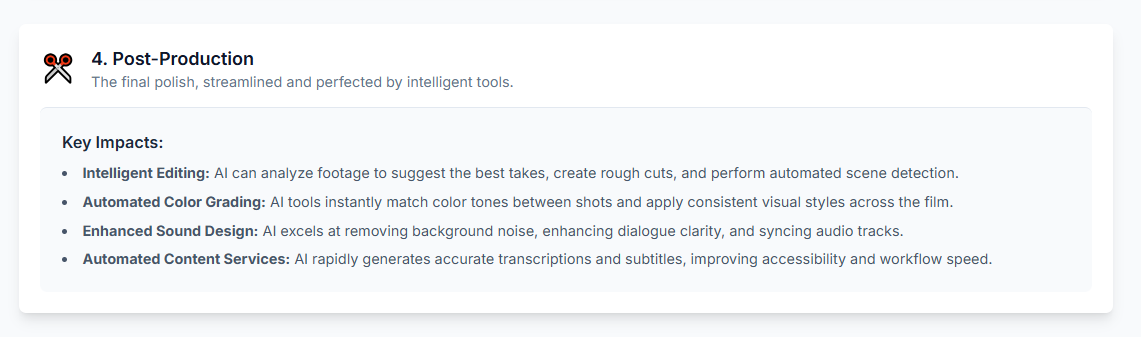
Beyond the Page: The Intelligent Script and Streamlined Pre-Production
The true revolution in AI-assisted rewriting lies in its ability to bridge the gap between creative development and the logistical demands of production. When a screenplay is refined using AI, it becomes a dynamic, queryable database—an “intelligent script”—that serves as the central hub for automating the most complex and time-consuming aspects of pre-production.
Automated Script Breakdowns
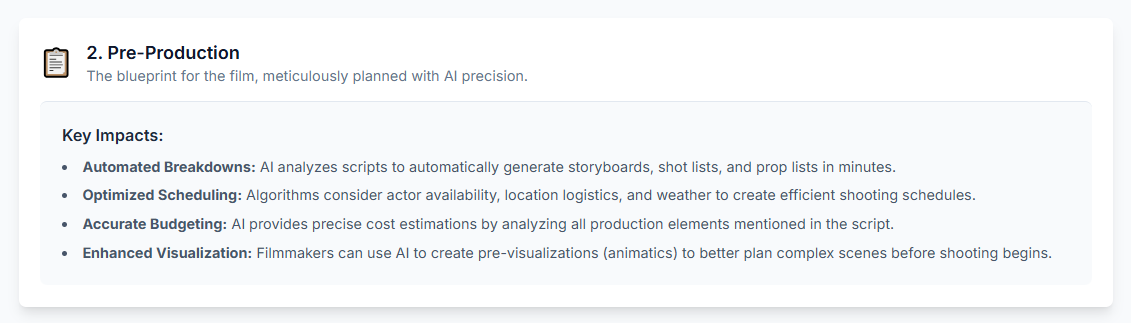
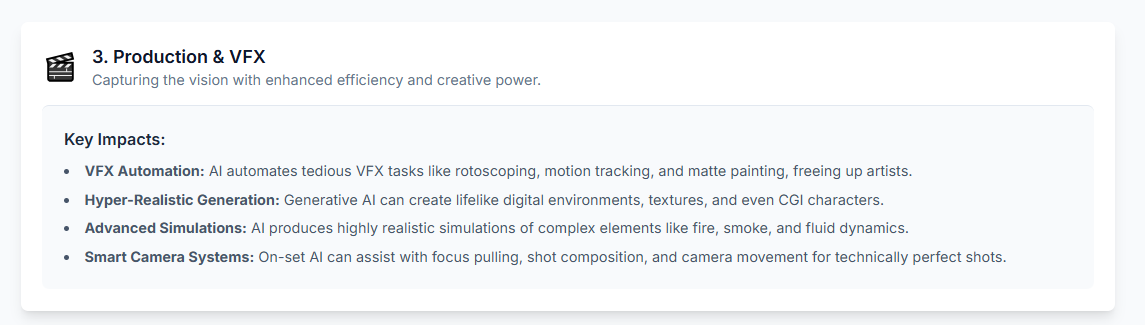
Traditionally a painstaking manual process, AI-powered software can now scan a 120-page script in minutes, automatically identifying and tagging every critical production element. Platforms like Filmustage and NolanAI parse the text to generate comprehensive lists of cast members, props, costumes, vehicles, sound effects, visual effects (VFX), and locations. This rapid and accurate breakdown saves production teams days or even weeks of labor, providing the raw data for all subsequent planning.
Smart Scheduling and Budgeting
This data directly fuels intelligent scheduling and budgeting tools. By extracting breakdown elements, AI systems can generate automatic time estimates for shooting each scene and organize them into an optimized shooting schedule. Concurrently, the same data is used to create highly accurate preliminary budgets. The AI identifies key cost drivers—such as scenes requiring extensive VFX or expensive locations—and provides data-driven projections that allow producers to assess financial viability with greater confidence early in the process. A writer can learn that a simple scene set in an airport is a major budget driver and opt to rewrite it for a bus station, making a multi-million-dollar decision before the script is even finished.
A Single Source of Truth for Production
This deep integration elevates the screenplay to a “single source of truth.” In a traditional workflow, information is manually transcribed into dozens of disparate documents, creating a high potential for errors. With an intelligent script, a change made in one place—such as altering a prop—can automatically propagate across all connected production documents, from call sheets to budgets. This dramatically reduces errors, improves communication, and ensures the entire team is working from the same authoritative data.
An Evolving Toolkit: A Landscape of Modern AI Software
The market for AI screenwriting tools has rapidly diversified, offering a wide array of platforms catering to different stages of the pipeline. Understanding this landscape is critical for leveraging the right technology for the right task.
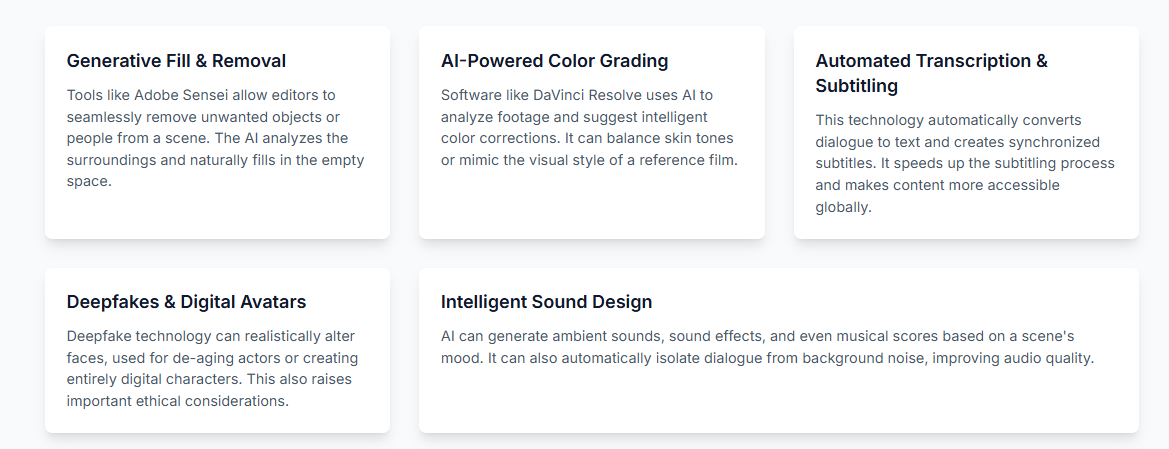
Generative Writing Assistants (The Creative Co-Pilot)
These tools function as direct collaborators in the act of writing. Platforms like Sudowrite excel at generating vivid sensory details and expanding scenes, while Jasper is adept at continuing a writer’s train of thought to break through creative blocks.
Analytical & Coverage Platforms (The AI Script Doctor)
These platforms provide data-driven feedback and market analysis. ScriptBook, for example, analyzes a screenplay to generate predictions on its potential box office performance and target demographics, offering studios a quantitative risk-assessment tool. Prescene offers AI-generated script coverage, character arc analysis, and market comparisons.
Integrated Production Suites (The End-to-End Solution)
These tools aim to connect the writing process directly to pre-production. NolanAI offers an AI co-pilot for writing, automated script breakdowns, and scheduling features. Filmustage excels in its powerful production breakdown capabilities, automatically tagging every element in a script.
Specialized Media & Voice Tools
These tools focus on generating other crucial assets from the script. Descript offers script-based audio and video editing with highly realistic voice cloning, while Respeecher provides studio-grade voice synthesis for automated dialogue replacement (ADR) and de-aging actors’ voices.
Tool |
Primary Function |
Key Features |
Target User |
Sudowrite |
Generative Writing |
Scene expansion, descriptive prose |
Fiction Writers, Screenwriters |
Prescene |
Script Analysis |
AI coverage, market comparison |
Producers, Studios, Writers |
NolanAI |
Integrated Production |
AI Co-Pilot, auto-breakdown, scheduling |
Indie Filmmakers, Producers |
Filmustage |
Production Breakdown |
Auto-tagging, storyboarding, reports |
Line Producers, ADs, Studios |
Descript |
Voice & Video |
Voice cloning, AI avatars |
Podcasters, Content Creators |
Respeecher |
Voice Synthesis |
High-fidelity voice cloning, de-aging |
Major Studios, Post-Production |
Navigating the New Frontier: The WGA Agreement and Creative Integrity
The rise of AI has raised legitimate concerns about creative homogenization, algorithmic bias, and the preservation of the “human spark.” An over-reliance on algorithms trained on past commercial successes could lead to a cinematic landscape that is polished and predictable but lacks a unique authorial voice.
These concerns were at the heart of the 2023 WGA strike, which resulted in a groundbreaking agreement that establishes foundational principles for AI’s role in the creative process. The agreement unequivocally states that AI cannot be considered a “writer” and any text it generates cannot be defined as “literary material.” This prevents studios from using AI to undermine a writer’s credit or compensation. The agreement also ensures a writer’s autonomy: a company cannot require a writer to use AI software.
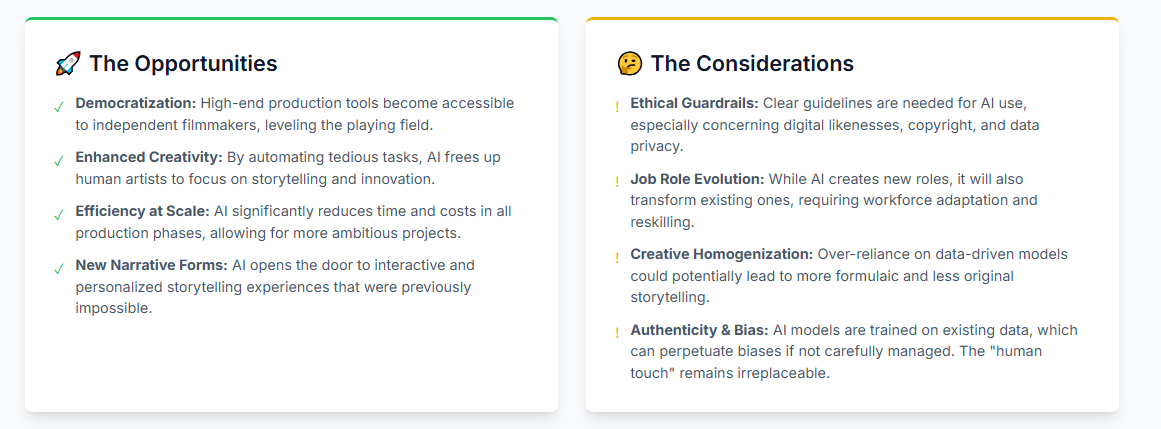
This framework sets the stage for future legal battles, particularly over the use of copyrighted scripts to train AI models. While the technology’s role as a tool is being codified, its capacity to supplant the human author remains a deeply contentious issue, with the industry drawing a clear line: AI is an acceptable tool to help execute a vision, but not to be the source of that vision.
As AI continues its exponential evolution, the screenwriter’s role will shift. The future will belong to those who can artfully blend human ingenuity with algorithmic power, combining traditional storytelling craft with proficiency in prompt engineering and AI curation. Amid this technological transformation, the core tenets of great storytelling—emotional depth, lived experience, and the ineffable “human spark”—will become more valuable than ever. The future of filmmaking lies in this powerful symbiosis: human empathy providing the soul, while AI optimizes, accelerates, and scales the execution.